Stay Ahead, Market Insights April 11th, 2024.
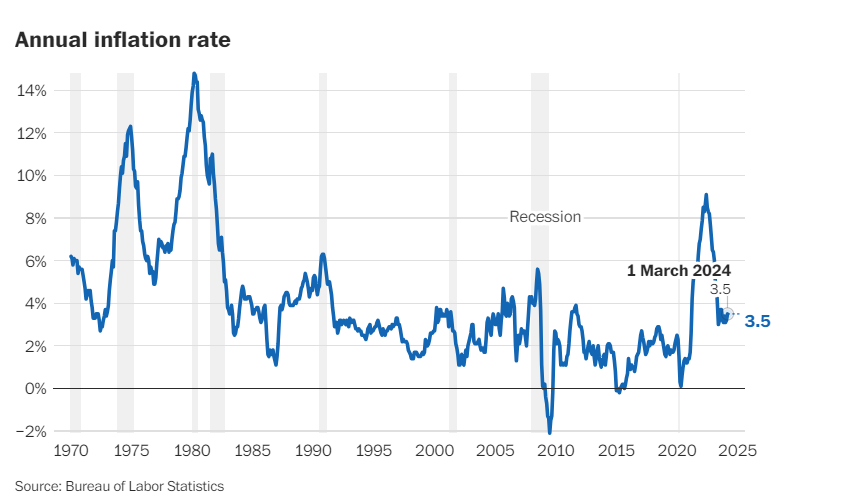
In March 2024, inflation rose to 3.5%, up from February’s 3.2%, signaling sustained economic stability and delaying expected interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. Energy and housing costs played significant roles, potentially impacting the upcoming November elections. Despite policymakers’ efforts, challenges persist in managing inflation’s effects, as the Fed aims to achieve its 2% inflation target amidst economic uncertainties.
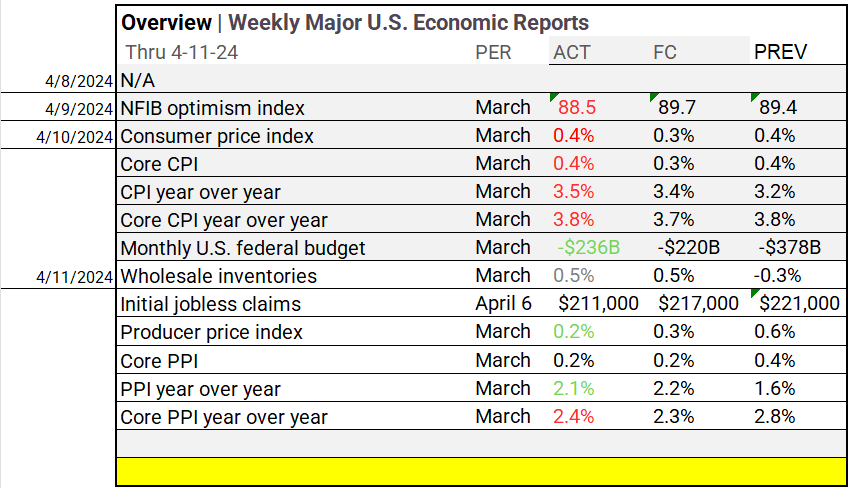
Traders are now betting on the Federal Reserve to potentially initiate interest-rate cuts as early as its late-July meeting, driven by a recent government report showing that producer prices in March increased slightly less than expected. March also saw consumer prices exceed expectations for the third consecutive month, prompting traders to adjust their forecasts, pushing back anticipated Fed rate cuts from June to September.
Market sentiment towards rate cuts has shifted, with Fed funds futures contracts for December indicating expectations of approximately 60 basis points in cuts this year, down from the 150 basis points projected at the start of 2024. According to CME Group data, the likelihood of a 25 basis point cut in June decreased from 57% to 49% in just a week.
March witnessed a modest increase in wholesale inflation, slightly below projections. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the producer price index (PPI) for final demand rose by 0.2% month-over-month, falling short of the expected 0.3% surge. However, non-seasonally adjusted data showed a 2.1% year-over-year increase, slightly below the forecasted 2.2% growth, reaching its highest level since April 2023.
Core PPI, excluding food and energy, increased as anticipated by 0.2%, with a non-seasonally adjusted annual acceleration to 2.4%, surpassing the predicted 2.3% growth, reaching its peak since August 2023.
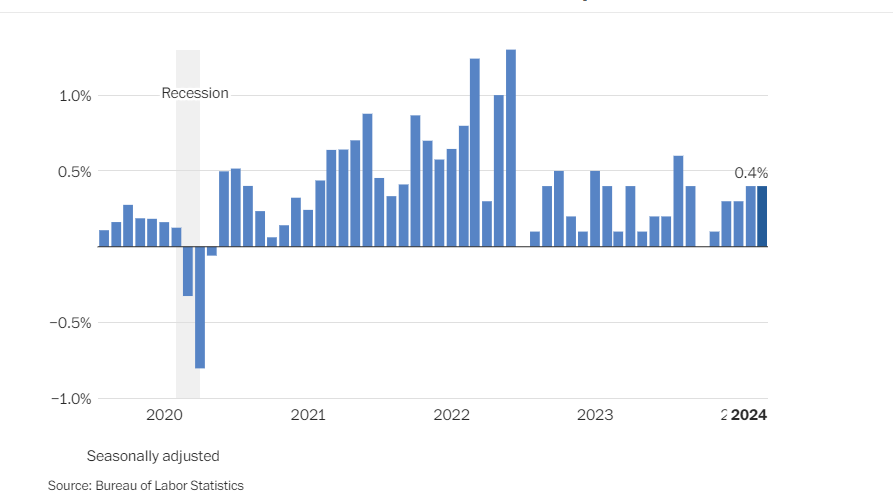
These wholesale price movements are critical indicators for potential consumer inflation. The Federal Reserve remains vigilant as it navigates inflationary pressures, mindful of their implications for monetary policy and economic stability. The correlation between PPI and CPI underscores the significance of these figures in assessing broader economic trends.
Yet, questions persist about the Fed’s future actions and the looming possibility of a recession. As inflation dynamics evolve, policymakers and market participants remain attentive to signals of economic shifts.




